How a Septic Works

Learn about septic systems
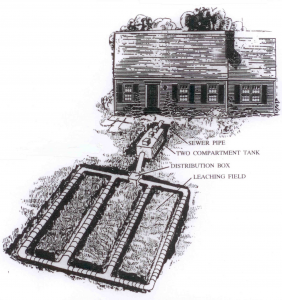
The purpose of a septic system is to treat household waste. A basic septic system consists of a large tank, a distribution box, and a leaching system.
1) Whenever you turn on a faucet, flush the toilet, do a load of dishes or laundry, the waste leaves the house through the main sewer line and enters the septic tank through the inlet pipe.
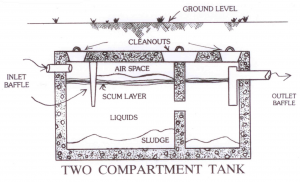
2) The septic tank prepares the waste material for disposal into the leaching system. Solids are kept within the tank by devices called baffles, which are located near both the inlet and outlet of the septic tank. While the heavy solids sink to the bottom forming a layer of sludge, the lighter solids float to the top. Bacteria living inside the tank help to break down the solids.
3) The remaining liquids flow through the outlet pipe to the distribution box where they are uniformly distributed through the leaching system.
4) The leaching system helps purify the liquids by filtration through the soil. A leaching system may consist of leaching fields, trenches, beds, galleries, or leaching pits (dry wells).
See the diagram below to further understand how your septic system works.